There are many kinds of oral lesions. While some of them need to be addressed right away due to their invasive nature. Others only look threatening and are not considered suspicious. Mucocele is among those oral lesions. While Mucocele looks scary it is a very common lesion found in the oral cavity. According to the Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, they affect 2.4 of every 1000 individuals.
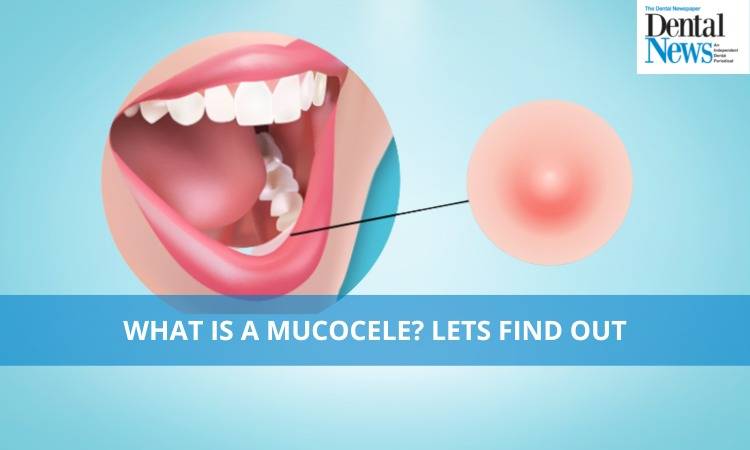
An oral mucocele will look like a soft, dome-shaped lesion in your mouth. They’re usually clear or have a bluish tone, and they vary in size from 1 millimetre to 2 centimetres wide.
The blue blister often is located on the lower lip. Other common sites include inside the cheek, surface of the tongue and mouth. These blue blisters are painless, appear round and don't contain any fluid. While a Mucocele might be painless and not a health hazard, it often interferes with speaking, eating and drinking.
While the peak age of mucoceles is considered between 10 and 20 years old, it can also happen between age 3 and 20 which makes up about 70% of the cases.
What Causes a Mucocele?
Typically mucoceles are a result of trauma to the salivary gland which results in spilling and accumulation of fluid in the connective tissue. The confined accumulation of fluid forms a cyst which can be distinguished from other cystic lesions. The types of trauma can include lip biting, cheek biting and constant contact with a sharp tooth, or continually thrusting the tongue against the teeth.
Diagnosis Of A Mucocele
While mucoceles are often diagnosed on clinical examination and based on the patients' symptoms- the diagnosis can be confirmed via one of the following tests and scans.
Biopsy: A biopsy includes extracting the tissue from the cyst for examination.
Doctors may require a biopsy in cases where
the mucous cyst is larger than 2 centimetres, the cyst’s appearance suggests adenoma (cancer) or lipoma and when there is no history of trauma.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound can create real-time images or videos with the help of high-frequency sound waves.
CT scan: CT scan is done when there is an extreme case of ranula extending the tissues in the neck.
Treatment Options
Most mucoceles rupture and resolve on their own. However, for cysts that repeatedly come back or for large mucoceles, your healthcare provider may recommend the following treatment options.
Cryotherapy: The procedure involves applications of extreme cold to freeze and destroy the mucocele cyst.
Laser treatment: A special laser is used to remove the lesion by a licensed healthcare provider.
Surgical excision: It is done under the supervision of an oral surgeon or dentist who will cut out and remove the cyst. They may also remove the salivary gland.
If you’re a regular lip or cheek biter, breaking these types of habits is the way to go. Keep a journal and keep track of how often you bite — it’s most likely related to stress, anxiety, or boredom. Once you’ve identified the triggers, you can try to find ways to stop biting your lips and cheeks. Chewing on sugarless gum is one method you can use to satisfy the urge to bite without harming yourself.
While home remedies might help heal some mucous cysts, you must avoid self-diagnosis. Your doctor can make sure the bumps aren’t related to something more serious, such as oral cancer.

Dr Rida Qamar
The author is contributing writer at Dental News Pakistan and can be reached at Ridaqamar100@gmail.com

